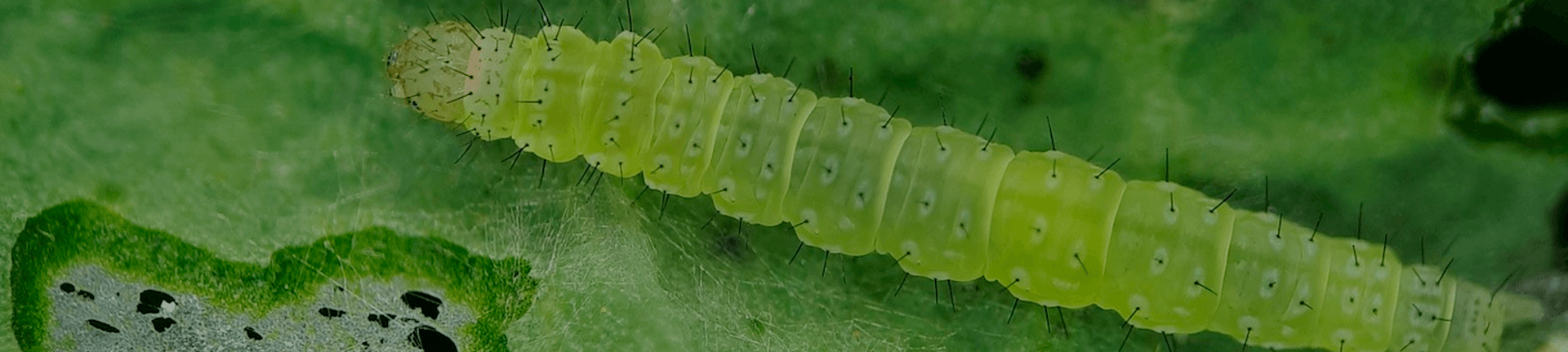

Cruciferous moth
Scientific name: Plutella xylostella
Crop: cabbage
Damage: defoliation, mainly in abaxial face of the leaves. In cabbage, the attack of this pest is observed from the formation of the cabbage head until harvest.
Behavior: Eggs are laid mostly on the abaxial face of the leaves, near the leaf ribs. After hatching, the larvae penetrate the leaves and build galleries. As they reach the second and third instars, the larvae abandon the galleries and start to feed mainly on the abaxial epidermis of the leaves. In the fourth instar, the larvae consume all the leaf. Pupae are formed in all parts of the plant, preferably in hidden places, sheltering themselves from natural enemies and climatic factors.
Bacillus thuringiensis has different crystals in its composition: Cry1Aa, Cry1Ab, Cry1Ac, Cry2Aa, and Cry2Ab. This characteristic makes Bacillus thuringiensis an important tool for the management of the complex resistance system of caterpillars.