Scientific name: Ecdytolopha aurantiana
Crop: citrus
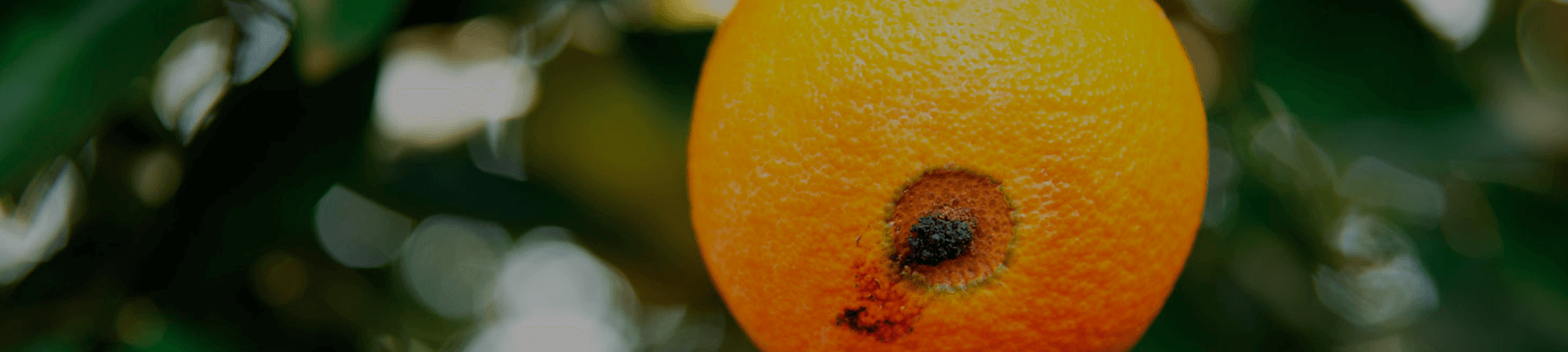
Damage: Fruit drilling: the fruits affected turn yellow and drop. The hole for caterpillar penetration become evident and it is possible to observe secretions that harden and stick to fruit peel.
Behavior:
- The moths lay eggs mainly on the fruit surface.
- After the hatching of the eggs, the caterpillars penetrate into the fruits and feed on the pulp.
- After penetrating into the fruit, the Ecdytolopha aurantiana releases excrements and food waste to the outside of the fruit, hardening the peel.
- At the end of the larval period, the caterpillars abandon the fruits to pupate in the soil.

Ecdytolopha aurantiana Photo: Fundecitrus

Fruit with symptoms of attack of Ecdytolopha aurantiana Photo: Fundecritus

Fruits dropped to the soil due to the attack of Ecdytolopha aurantiana Photo: Heraldo Negri-ESALQ

Adult female of Ecdytolopha aurantiana Photo: Heraldo Negri-ESALQ

Adult of Ecdytolopha aurantiana Photo: Fundecitrus
Control
End of caterpillar resistance!
Bacillus thuringiensis has different crystals in its composition: Cry1Aa, Cry1Ab, Cry1Ac, Cry2Aa, and Cry2Ab. This characteristic makes Bacillus thuringiensis an important tool for the management of the complex resistance system of caterpillars.