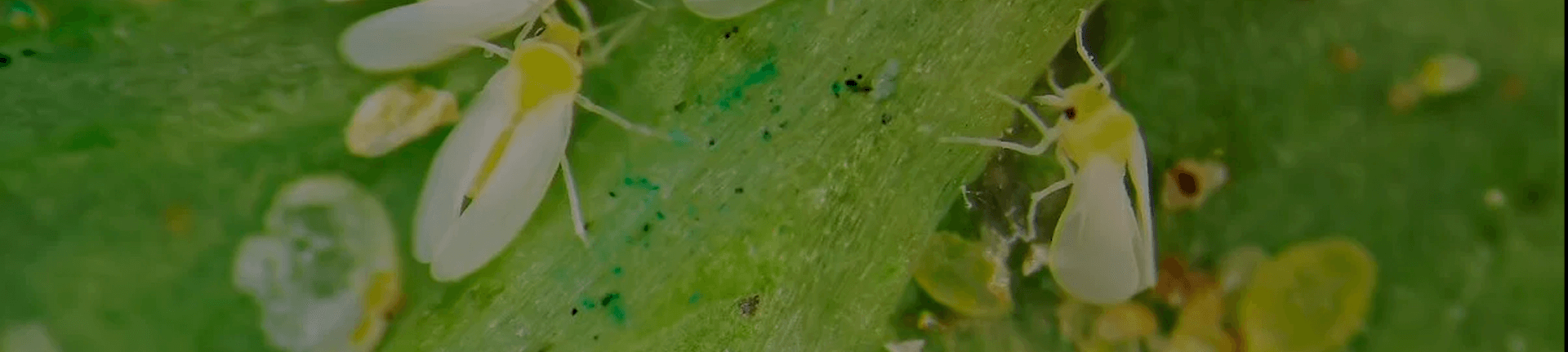

White Fly
Scientific name: Bemisia Tabaci (Gennadius, 1889)
Crops: soybean, bean, cotton, and green-leafy vegetables.
Behavior: Adults and nymphs generally occur on the lower part of plants and have high mobility. Females are usually larger than males and can lay up to 100 eggs on the abaxial face of the leaves. In the nymph phase (4 instars), the insect remains fixed on the abaxial face of the leaves (immobile phase). Similarly, the pupal phase is also immobile. The white fly causes damages by sucking the sap from the leaves (direct damage), causing sap loss and leading to the formation of fumagina (fungus) on the leaf, compromising the photosynthetic activity (indirect damage). The white fly is also the vector insect of viruses.
Life cycle: incubation period: > 7 days; nymph period (4 instars): > 14 to 28 days; adult period: > 18 days.
Diseases: Vector of soybean mosaic virus (SMV), curly mosaic virus (VMCrS), stem necrosis (CMMMV), bean golden mosaic virus (BGMV), yellow mosaic virus (CpMMV), cowpea mild mottle virus (CpMMV), cotton mosaic virus (AvMV), and geminiviruses in vegetables.
Latria is a biological insecticide and acaricide composed of the microorganism Beauveria bassiana.