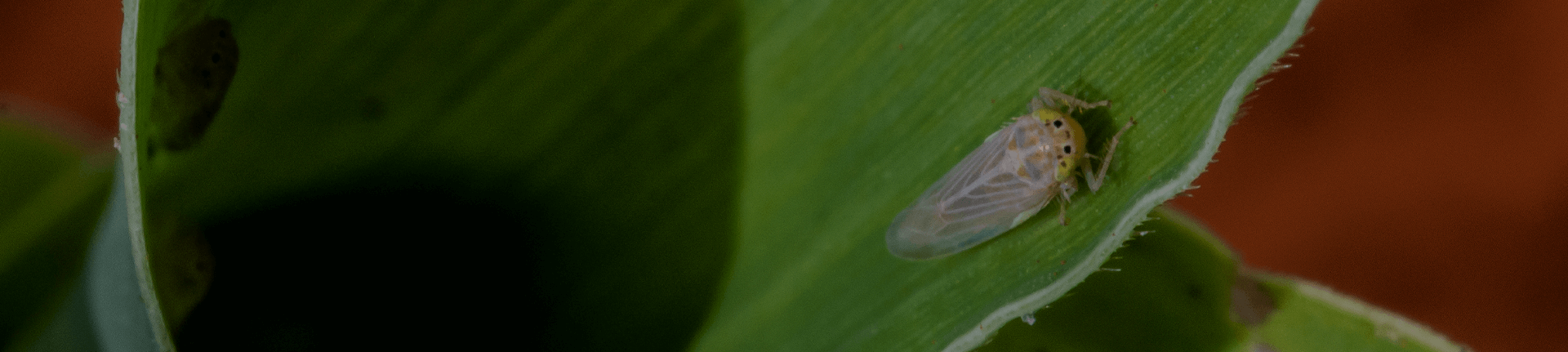

Corn leafhopper
Scientific name: Dalbulus maidis
Crop: corn
Behavior: Corn leafhoppers usually occur in the corn cartridge with high mobility between cropped fields. The pest incidence varies according to climatic conditions, favored by low rainfall and high temperatures. The damages consist of sucking the sap (direct damage) and transmission of mollicutes and viruses (indirect damage), while the direct damage is more relevant in terms of crop yield. The female leafhopper can lay from 400 to 600 eggs within a 4-6 day period. This species reproduces only in the corn crop, but it can survive in other grass species, such as sorghum (up to 3 weeks) and millet (up to 5 weeks).
Life cycle: incubation period: > 8 to 10 days; nymph period: > 15 to 17 days; adult period: male = 16 days and females = 42 days.
Diseases caused: vector of maize bushy stunt phytoplasma (MBSP), corn stunt spiroplasma (CSS) and maize rayado fino marafivirus (MRFV).
Latria is a biological insecticide and acaricide composed of the microorganism Beauveria bassiana.